Java集合-初读HashMap源码
- Qingfeng Zhang
- Java , Data structure
- April 30, 2020
Sections
哈希表(散列表)是根据设定的哈希函数和冲突处理方法把一组关键字映射到一个有限的地址空间,存放关键字及其对应的值的表称为哈希表或散列,哈希冲突主要取决于:哈希函数、冲突处理方法、负载因子的大小;常用的哈希冲突解决方法:
1.开放地址法:线性探测、二次探测
2.链地址法
3.再哈希法
4.建立公共溢出区域
HashMap解决哈希冲突中的链地址法就是将数组和链表结合在一起,发挥两者的优势;HashMap继承了AbstractMap类,同时实现了Map等多个接口;
java
1.8之前HasMap和其它的map都是通过链地址法解决冲突,这种方法在最坏的情况下会使HashMap的性能降低到O(n),为了解决这个问题,java
1.8中使用红黑树代替链表解决冲突,当链表中元素的数目达到一定值会将链表转化为红黑树,这样最坏情况下的性能也有O(logn);
HashMap类的参数:
// 序列化ID
private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L;
// 默认的初始容量16,即桶的数量
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// 最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认装载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 当桶的元素数量大于8将链表转换为红黑树
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 当桶的元素数量小于6将树还原成链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 最小树形化容量:当哈希表容量小于这个值时才允许树形化链表
// 否则桶内元素太多就直接扩容了,为避免扩容和树形化的冲突不能小于4*TREEIFY_THRESHOLD
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
Node类是HashMap的一个静态内部类,其实现了Map接口的内部接口Entry,Node类以链表节点的形式定义了哈希表中的键值对:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; //哈希值,不可变
final K key; //键,不可变
V value; //值
Node<K,V> next; //下一个节点
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
// 重写toString方法
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
// 重写Object的hashCode()方法,将key的hashCode与value的hashCode进行异或运算
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
//重写Object的equals()方法,判断依据是键相等且值相等
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
此外,HashMap中关键变量如下:
// 存放Node节点的数组
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
// 存放Node节点的集合
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
// HashMap存放的数据个数
transient int size;
// 记录HashMap的修改次数
transient int modCount;
// 当HashMap大于threshold会进行resize
int threshold;
// HashMap的装填因子
final float loadFactor;
由上面的代码可以看出HashMap包含一个Node数组table,每一个Node可以看作一个链表表头节点,table的每一个位置可以看作是一个桶(bucket),桶中存放的是发生哈希冲突的节点组成的链表;

HashMap的构造方法:
public HashMap() {...} //默认容量16,装填因子0.75
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {...}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {...}
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {...} //根据一个map构造HashMap
HashMap类的hash()方法:
HashMap类的hash()方法用于计算key的哈希值,计算方式是将key的hashCode()值与右移16位的结果进行异或运算,简单来说就是将高位的值和低位的值进行结合,降低哈希冲突的概率;
1.7版本中的hash()方法的计算方式更复杂一点,并且还有计算哈希表索引的indexFor()方法,在1.8中hash()的计算简化,并且将indexFor()的计算放在了各个方法里;
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
根据hash()的结果计算索引是直接使用位运算&实现的,相比于取模运算更快;
如果length等于2的n次方,h%length = h&(length-1),如当length=8,也就是1000,则length-1是0111,h&(0111)相当于取h的后三位,也就是h%length;
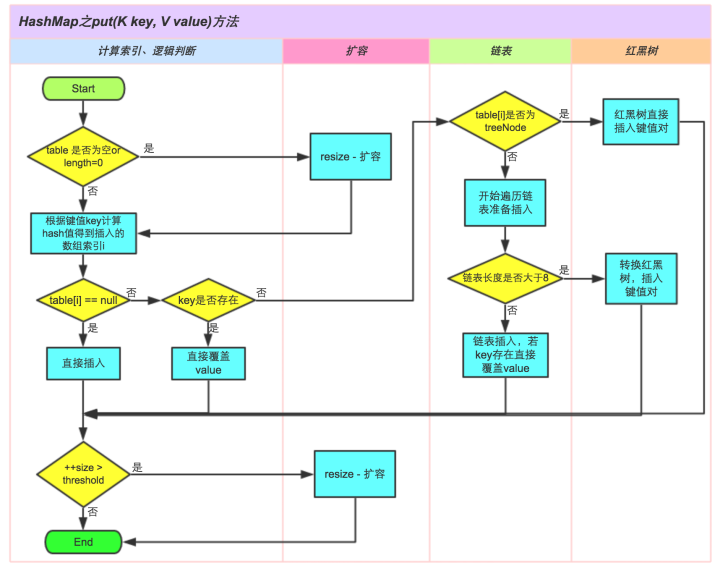
HashMap类的put()方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
Node<K,V> p;
int n, i;
// 如果table为null或长度为0则创建一个table
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 计算索引的位置,如果该位置没有元素就创建node放入
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else { // 否则说明该索引位置有元素
Node<K,V> e;
K k;
// 判断想要放入的节点是否已经存在
//节点的hash()相同并且key的值或地址相等就认为两个节点相等,直接更新value
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 如果是红黑树就在树中插入节点
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
// 否则的话就在链表中插入
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 如果链表长度超过阈值则转换成红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 如果的插入节点key已存在则覆盖
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// key已存在则返回旧的value
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 说明没有相同的key,插入一个key-value,结构变化+1
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
put()的过程如下图所示:
HashMap类的get()方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
// 如果表不是null、长度不为0且要查找的位置不为空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 检查第一个节点是否是要找的
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 否则从第二个节点开始找
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 如果是红黑树则在树种查找
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 否则在链表中查找
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
HashMap的扩容
HashMap的初始大小为16,当包含的元素超过装载因子就进行扩容,每次扩容为原来的2倍,扩容之后元素的位置要么不变,要么是在原位置移动2次幂,如:当从16扩容到32,假设原来hash(key)是30,计算的索引是30&(16-1)=14,扩容之后就是14+16=30;

因此扩容之后只需要判断原来的hash(key)对应2*oldCap-1高位的是否为1,如:31的最高位为16,对应30该位为1,因此需要修改key为新索引,否则位置不变;